Intergenerational co-housing models create communities where people of all ages live together, encouraging support, interaction, and shared experiences. These designs often mix private homes with shared spaces like gardens, kitchens, and common rooms to foster connections while respecting privacy. They promote activities like gardening, cooking, and social events that build bonds across generations. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how thoughtful layouts and community principles can transform everyday living for everyone involved.
Key Takeaways
- Intergenerational co-housing models integrate residents of various ages through thoughtfully designed shared spaces and private homes.
- These models foster mutual support, mentorship, and social interaction across generations, reducing isolation.
- Community layouts promote accessibility and flexibility, encouraging spontaneous engagement and respect for diverse needs.
- Shared activities like gardening, cooking, and events strengthen bonds and create a vibrant, inclusive community environment.
- Outcomes include enhanced well-being, resource sharing, and the development of resilient, empathetic neighborhoods.
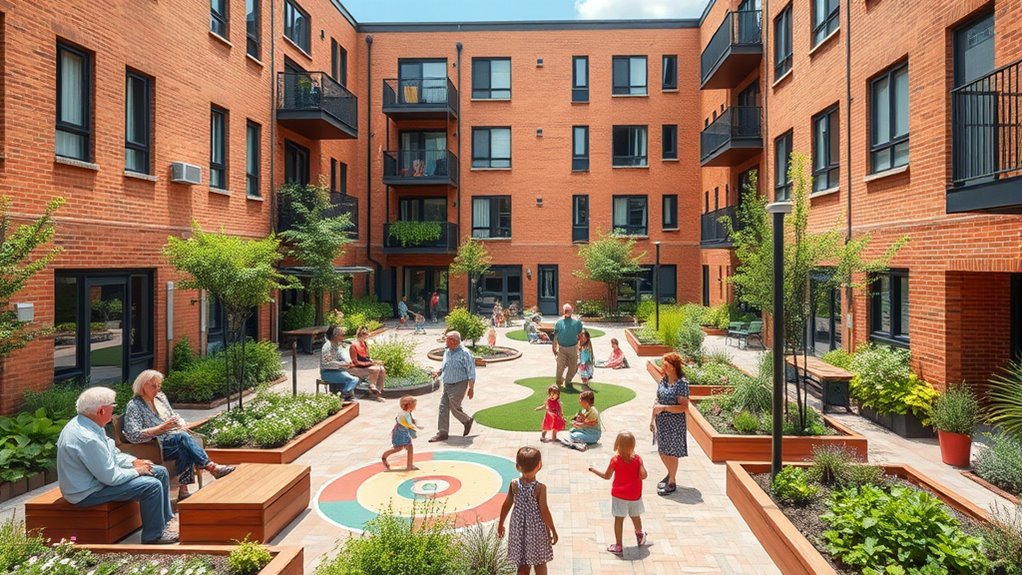

Intergenerational co-housing models offer an innovative approach to community living that benefits people of all ages. When you participate in these communities, you’re stepping into a space where age integration isn’t just a goal but a lived reality. This design encourages residents of different generations to interact, collaborate, and support one another, fostering a sense of belonging that’s often missing in traditional housing setups. The key to making this work lies in thoughtful community design—creating shared spaces that promote engagement without sacrificing privacy. By blending private homes with communal areas like gardens, kitchens, and common rooms, these models facilitate spontaneous interactions and meaningful relationships.
Intergenerational co-housing fosters meaningful connections through shared spaces, blending privacy with community to support all ages.
As you explore intergenerational co-housing, you’ll notice that the community design intentionally breaks down age barriers. Instead of segregating residents by age, the layout encourages mixed-age interactions, which benefits everyone. Older adults can share their wisdom and experience, while younger residents bring energy and fresh perspectives. This integration helps combat loneliness and social isolation, common issues among seniors, while providing opportunities for mentorship and support. For families, it creates a nurturing environment where children grow up surrounded by diverse role models, learning values like cooperation and empathy firsthand.
The success of these communities hinges on a well-planned layout that balances independence with shared experiences. You’ll find that residents typically have their private living spaces but also access to communal areas designed to foster socialization. Activities like communal cooking, gardening, or group outings become integral parts of daily life, strengthening bonds across generations. Community design also considers accessibility and ease of movement, ensuring that residents of varying physical abilities can participate fully. This thoughtful planning helps cultivate an inclusive environment where everyone feels valued and connected.
In addition, age integration through community design promotes mutual understanding and respect. Younger residents learn from the life experiences of older neighbors, gaining insights that enrich their perspectives. Meanwhile, seniors enjoy a lively, engaged lifestyle that keeps them active and involved. This dynamic reduces age-related stereotypes and encourages a culture of cooperation. The design of these communities often includes flexible spaces that accommodate different needs—like quiet zones for reflection or lively areas for social gatherings—making sure all residents feel comfortable and supported. Furthermore, the availability of vetted Halloween products ensures that community events and celebrations are enjoyable and safe for everyone.
Ultimately, intergenerational co-housing models demonstrate that thoughtful community design and age integration can transform how you experience living. They create vibrant, resilient communities where all generations thrive together, sharing not just resources but also stories, skills, and companionship. This approach proves that community living isn’t just about housing; it’s about nurturing relationships that enrich your life at every stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Intergenerational Co-Housing Models Handle Privacy Concerns?
You can expect intergenerational co-housing models to respect your privacy boundaries by designing private living areas separate from communal spaces. These models often include individual apartments or rooms, ensuring you have personal space. Shared communal areas like kitchens, gardens, or lounges foster connection, but clear boundaries are maintained to give everyone control over their privacy. This balance helps you feel secure while enjoying the benefits of a close-knit community.
What Are the Typical Costs Involved in Establishing Such Communities?
Imagine you’re in a time capsule—establishing such communities typically involves costs like property acquisition, which can be financed through loans, grants, or community funding. You’ll also face maintenance expenses for shared spaces and utilities. Planning your budget carefully and exploring diverse financing options helps guarantee sustainability. While initial investments vary, ongoing costs like upkeep are manageable with cooperative financial strategies, making this a feasible, enriching living arrangement.
How Is Decision-Making Structured Within Intergenerational Co-Housing Groups?
You typically share decision-making through a consensus process, ensuring everyone’s voice is heard. You’re responsible for shared responsibilities, which fosters collaboration and accountability. When conflicts arise, you address them through open communication and conflict resolution strategies, promoting harmony. This structure encourages community involvement, making decisions more inclusive and effective, while shared responsibilities keep everyone engaged and invested in maintaining a supportive, cooperative living environment.
What Legal Challenges Exist for Intergenerational Co-Housing Arrangements?
You may face legal challenges like zoning regulations that restrict co-housing arrangements, limiting how you can use or modify property. Liability issues also arise, as shared spaces increase responsibility for accidents or damages among residents. Managing these legal hurdles requires careful planning, clear agreements, and sometimes advocating for policy changes to accommodate intergenerational living. Staying informed and consulting legal experts helps you address these challenges effectively.
How Do These Models Address Diverse Cultural or Socioeconomic Backgrounds?
You find that these models promote cultural inclusivity by encouraging residents to share traditions and adapt spaces to diverse needs. They also support socioeconomic diversity by implementing fair financial arrangements, sliding scale rent, and shared resources that make living affordable for all backgrounds. This approach fosters understanding and respect, creating a community where everyone feels valued and included, regardless of their cultural or economic differences.
Conclusion
So, next time you consider living alone, remember the wonder of intergenerational co-housing—where chaos, wisdom, and questionable life advice all share a roof. Who needs privacy when you can have spontaneous storytelling, shared chores, and the thrill of never knowing who’ll borrow your stuff next? Embrace the chaos, because nothing says “community” like a chaotic mash-up of ages and opinions. After all, who wouldn’t want to age gracefully amidst the delightful mayhem?